This week Sens. Chuck Schumer and Bernie Sanders said they are working on legislation to curb company stock buybacks unless they pay a $15 minimum wage and offer better benefits to their workers, and Wall Street is firing back with one strategist noting: “Good companies buy back their shares.”
“Buyback activity is, if anything, a complement to other corporate activities that are more long-term in nature.”
Stock buybacks soared to a record $1.04 trillion in 2018 during a historic bull market fresh on the heels of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act that cut the corporate tax rate from 35 to 21 percent.
Schumer and Sanders argue that such a spike exacerbates income inequality because capital owners have seen their portfolios and wealth grow in value while middle management down to the working class deal with meager-to-flat wage increases.
Per CNBC:
Buybacks aggravate inequality
Taking these claims in order, the senators hold that share buybacks don’t benefit the vast majority of Americans.
When a stock buyback occurs, a company chooses to use its excess cash to repurchase a predeteremined amount of its own stock. Repurchased shares are absorbed by the company, and the number of outstanding shares on the market is reduced. That has the effect of enriching those who’d then own a relatively larger slice of a company by making each share more valuable.
Even armed with statistics from Goldman Sachs it’s not difficult to see how this could widen the income gap between the nation’s richest and poorest households.
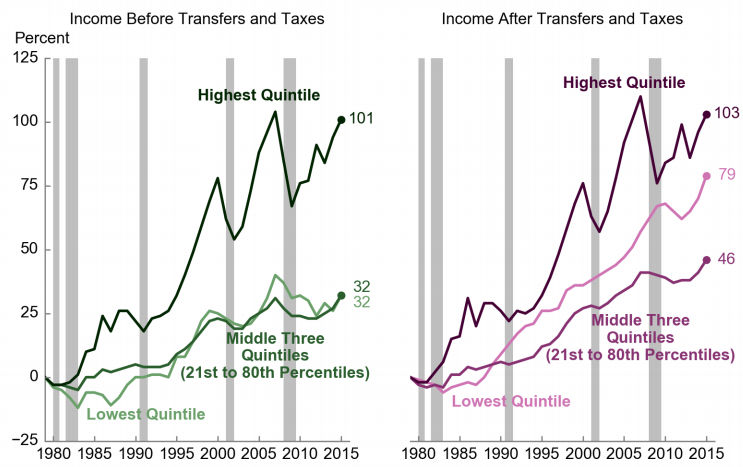
“It is indeed true that stock ownership has become more concentrated,” Goldman’s chief economist, Jan Hatzius, wrote last month. The wealthiest 0.1 percent and 1 percent of households now own about 17 percent and 50 percent of total household equities, respectively, up significantly from 13 percent and 39 percent in the late 1980s.
“Over the past several decades, corporate boardrooms have become obsessed with maximizing only shareholder earnings to the detriment of workers and the long-term strength of their companies, helping to create the worst level of income inequality in decades,” the senators wrote.
According to the most recent Census data, the bottom 20 percent of households earned 3.5 percent of the nation’s income while the richest 5 percent kept 21.8 percent of the pie, down from 22.8 percent in 2016. Households in the lowest quintile had incomes of $24,638 or less in 2017, while the top 5 percent of households in the income distribution had incomes of $237,035 or more.
Lloyd Blankfein, the former CEO of Goldman Sachs, is correct that the money from stock buybacks “doesn't vanish.” It increases the wealth of billionaires like him. Instead of making the very rich even richer, how about increasing wages for American workers. Is that a bad idea? https://t.co/FpIGQW9IZC
— Bernie Sanders (@SenSanders) February 5, 2019
Others, such as Stanford Law Professor Laurie Hodrick, challenge that opinion and argue that the more socially prosperous thing to do is to return residual monies to investors in the form of buybacks and dividends. Such a move would ensure the healthiest companies have access to the capital they need to grow their business and maximize employment, she said.
“The irony is that the thing to boost economic well-being in the long term would be to channel the capital to where it will contribute most to long-term prosperity,” Hodrick said Tuesday. “If you really want a long-term, robust economy that will hire and pay workers, the best way to do that is reallocate cash to investors.”
Corporations have been on a hiring binge lately with robust nonfarm payroll gains in the past 12 months. The unemployment rate ticked higher to 4 percent in January and more Americans re-enter the workforce. On a year-over-year basis average hourly earnings rose 3.2 percent, consistent with the past few months and around the highest levels of the recovery.
Buybacks impede a company’s reinvestment
The second claim made by Schumer and Sanders is that buybacks infringe on a company’s ability to reinvest in itself.
“When corporations direct resources to buy back shares on this scale, they restrain their capacity to reinvest profits more meaningfully in the company in terms of R&D, equipment, higher wages, paid medical leave, retirement benefits and worker retraining,” their column states.
Research and development spending as a percentage of GDP has remained largely constant in the United States over the past several years even with the surge in buybacks. Spending at businesses, government and higher education has hovered between 2.5 and 2.82 percent since 2005, according to the World Bank.
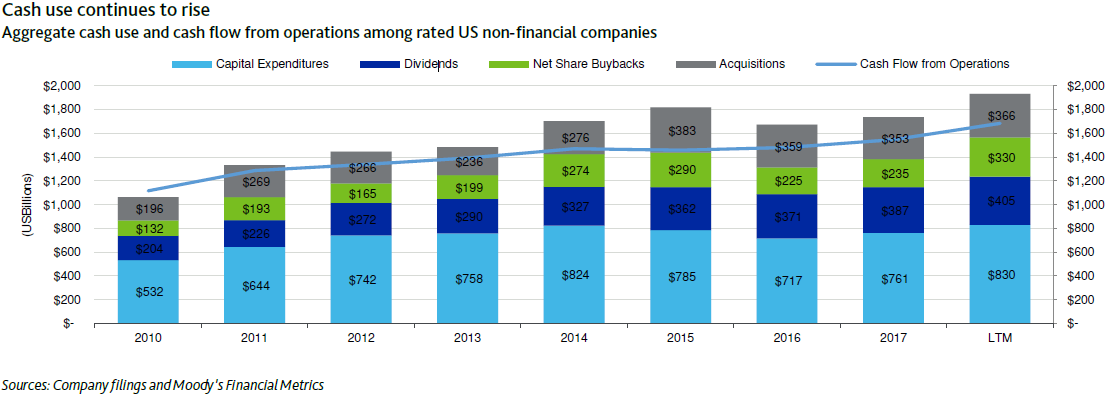
As of June 30, 2018, the top five cash holders of U.S. nonfinancial companies were Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, Cisco and Oracle, five enormous technology companies renowned for their reinvestment and innovation.
At that time, capital expenditures — funds used by a company to acquire, upgrade, and maintain property, industrial buildings, or equipment — consumed the largest portion of cash flow from operations. Capital spending totaled $830 billion for the 12 months ended June 30, up 9 percent from calendar 2017.
“Buyback activity is, if anything, a complement to other corporate activities that are more long-term in nature,” Bernstein’s Weisberger added.
“When looking across stocks in the S&P 500, a company’s buyback yield tends to be positively correlated with R&D spending and employment growth. While the correlations are modest, at the very least, buybacks are not coming at the expense of these other activities in a systematic way,” he wrote.